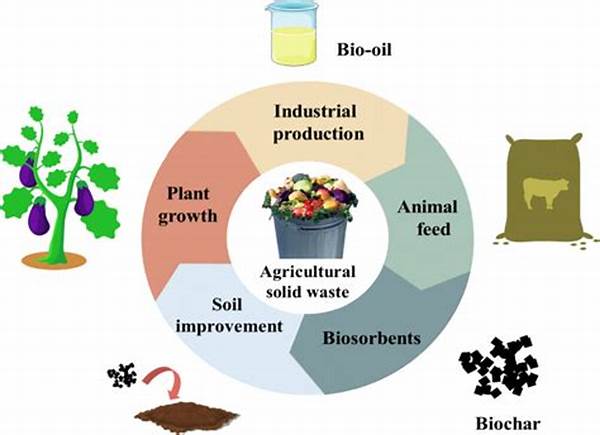
In recent years, the agricultural sector has increasingly recognized the imperative of minimizing waste in its operations. Waste reduction in agricultural practices is not only a matter of economic efficiency but also an issue of environmental sustainability. As natural resources become scarcer and environmental concerns grow, adopting strategies to reduce waste is essential for the long-term viability of agriculture. This article will explore various aspects and strategies of waste reduction in agricultural practices, highlighting their significance and impact.
Read Now : Advanced Api Threat Detection Systems
Importance of Waste Reduction in Agriculture
Waste reduction in agricultural practices bears considerable importance given its multifaceted benefits. Firstly, it enhances resource efficiency, thus reducing the cost burden on farmers and improving profitability. By optimizing the use of inputs such as fertilizers, water, and pesticides, waste is minimized, leading to better resource allocation and usage. Secondly, sustainable waste management practices mitigate the environmental impact of agricultural operations. By reducing the volume of waste that ends up in landfills, the agricultural sector can contribute more significantly to environmental conservation. Moreover, waste reduction in agricultural practices is vital in the fight against climate change. Agriculture is both a source and a sink for greenhouse gases; therefore, implementing waste reduction techniques can significantly decrease greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a healthier planet. In essence, minimizing waste ensures that resources are preserved for future generations, ensuring the sustainability of agricultural systems globally.
Strategies for Effective Waste Reduction
1. Resource Optimization: Waste reduction in agricultural practices involves optimizing input use, such as precision agriculture techniques, to ensure minimal wastage of water and nutrients.
2. Composting Techniques: Adopting composting methods transforms organic waste into valuable fertilizers, thus reducing dependency on chemical fertilizers and enhancing soil health.
3. Crop Rotation Systems: Implementing crop rotation helps in breaking pest cycles and reducing pesticide use, thus minimizing chemical waste.
4. Integrated Pest Management: This efficient approach leads to reduced pesticide waste through biological controls and monitoring, ensuring pest management is effective yet sustainable.
5. Waste Recycling Programs: Establishing recycling systems for agricultural plastics and packaging materials helps in drastically lowering the overall waste produced by farming operations.
Technological Interventions in Waste Reduction
Technological interventions play a crucial role in achieving waste reduction in agricultural practices. Precision agriculture, which utilizes data analysis, GPS, and IoT devices, enables farmers to apply resources with pinpoint accuracy. This targeted approach leads to a significant decrease in waste, particularly in water and fertilizer use. Another technological advancement is the use of bioengineered crops, which are designed to resist pests and diseases, thereby reducing the need for chemical interventions. These crops, often genetically modified or selectively bred, have enhanced resistance traits that contribute to minimal pesticide applications, thus cutting down on waste associated with chemical treatments.
Sensor technology also contributes significantly to waste reduction in agricultural practices by providing real-time data on soil conditions, crop health, and environmental parameters. These insights allow for timely interventions that ensure optimal resource utilization and minimize wastage. Furthermore, advances in waste-to-energy technologies enable the conversion of agricultural waste into renewable energy sources, providing farmers with sustainable energy solutions. These technologies not only enhance waste reduction but also offer an economic incentive by transforming waste into a value-added product. Thus, the integration of technology in agriculture is pivotal to advancing waste reduction efforts and ensuring the sector’s sustainability.
Challenges in Implementing Waste Reduction Strategies
Implementing waste reduction in agricultural practices is not without challenges. One of the primary obstacles is the financial investment required for acquiring advanced technologies. Although these technologies promise long-term savings and efficiency, the initial cost can be prohibitive for small-scale farmers. Moreover, there is often a knowledge gap regarding the latest waste reduction techniques, which can hinder effective implementation. Training and education are thus essential components for overcoming this barrier. Additionally, cultural resistance to changing traditional farming methods can impede the adoption of newer, more sustainable practices. Farmers may be reluctant to shift from conventional methods to innovative techniques due to uncertainties concerning effectiveness and profitability.
Read Now : Streamlining Processes With Apis
Government Regulations: While regulations can drive change, overly stringent policies may pose operational challenges for farmers trying to adopt waste reduction in agricultural practices.Market Dynamics: Fluctuating market demands and prices can influence the level of waste generated, often complicating efforts to maintain consistent waste reduction practices.Infrastructure Limitations: Lack of adequate infrastructure can hinder effective waste management and recycling efforts, particularly in rural and developing regions.Climate Variability: Climate change impacts, such as unpredictable weather patterns, can affect the implementation of waste reduction strategies, requiring adaptive approaches.
Benefits of Waste Reduction for Sustainable Agriculture
The benefits of waste reduction in agricultural practices extend beyond immediate cost savings and environmental impacts. Sustainable waste management fosters the resilience of agricultural systems by preserving soil health and biodiversity. Healthy soils rich in organic matter and diverse organisms contribute to improved crop yields and reduced dependency on synthetic inputs, thus creating a more sustainable agricultural framework. Additionally, reducing waste supports the livelihoods of farmers by lowering production costs and increasing market competitiveness.
Sustainable practices also enhance the social aspects of agriculture by promoting food security and supporting rural communities. By reducing waste, more efficient resource allocation ensures a stable food supply, crucial for feeding the growing global population. Furthermore, embracing waste reduction in agricultural practices aligns with international sustainability goals, thus positioning agriculture as a key contributor to global environmental efforts. Therefore, the cumulative benefits showcase waste reduction as an indispensable strategy for advancing agricultural sustainability.
Innovative Practices and Their Role in Waste Reduction
Innovative practices in agriculture often serve as catalysts for waste reduction. Techniques such as permaculture and agroforestry exemplify how integrated approaches can harness nature’s processes to reduce waste and improve ecosystem health. Permaculture emphasizes designing agricultural landscapes that mimic natural ecosystems, allowing for closed-loop systems where waste is minimized. Similarly, agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs into agricultural landscapes, which can improve nutrient cycling and reduce soil erosion.
Moreover, collaboration among stakeholders, including government agencies, research institutions, and the private sector, is paramount in fostering innovation. Shared knowledge and resources enable the development and dissemination of effective waste reduction practices and technologies. Engaging farmers in participatory research ensures that innovations are practical and applicable to local contexts, enhancing their adoption. In conclusion, innovative agricultural practices represent a forward-thinking approach to waste reduction, driving the sector towards a more sustainable and resilient future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, waste reduction in agricultural practices stands as a pivotal component in achieving sustainable agricultural systems. Through the adoption of advanced technologies, innovative techniques, and effective waste management strategies, the agricultural sector can significantly diminish its environmental footprint. The challenges, while substantial, can be addressed through the concerted efforts of all stakeholders involved. By embracing waste reduction methods, agriculture can enhance resource efficiency, support environmental conservation, and secure food production for future generations. The continued commitment to waste reduction in agricultural practices will not only safeguard our planet but also ensure the prosperity and well-being of communities worldwide.